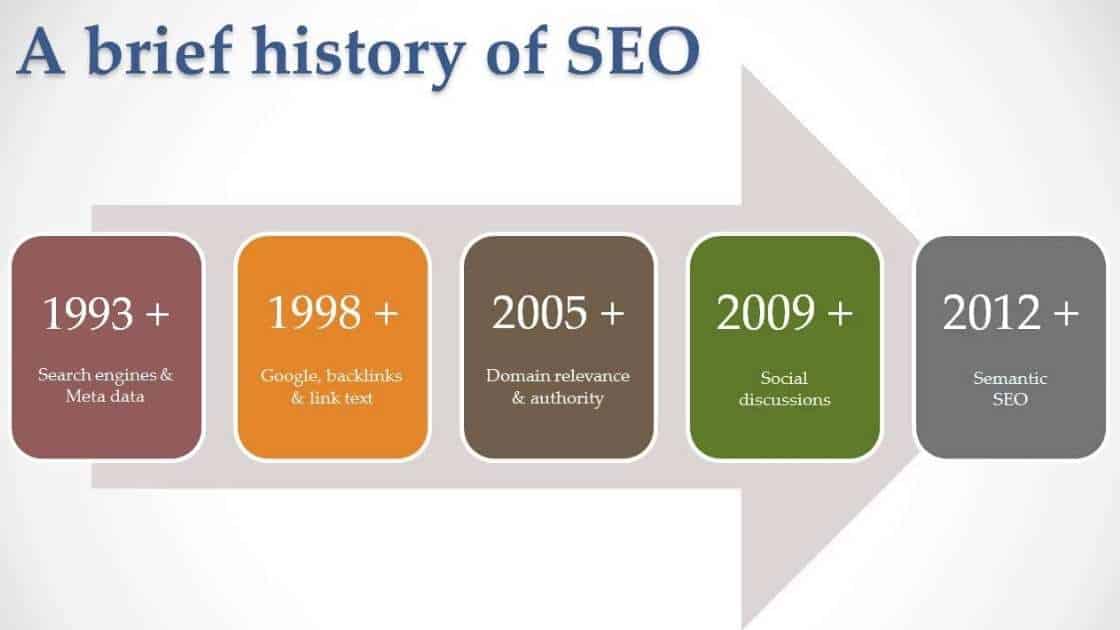
If you want to be king of the SERPs (search engine results pages) and increase your visibility for current and potential customers, you need to utilise SEO (search engine optimisation) tactics to get noticed and drive traffic to your website. But what is SEO and how has it changed over the years?
On 6 August 1991, Tim Berners-Lee, a computer scientist working at CERN in Switzerland, published the first ever website. As websites started popping up there was a need for a system to sort and categorise them to make them easily accessible. Thus, search engines arose, and with them SEO.
When you look for something on the internet a search engine, such as Google or Microsoft Bing, will sift through trillions of web pages and documents to find the best matches for your query. Search engines use algorithms to analyse what is being searched for and which results are the best fit. SEO tactics are your way of telling search engines what your website is about and where it should rank in the search engine’s results pages.
In the early days of the internet, optimising your web presence meant on-page activities such as relevant content, domain names, HTML tags, links and keywords, and repeating those keywords enough throughout your web pages. It was less about quality and more about quantity. So, to outrank your competitor, you’d simply double up on the keywords and increase the number of links to your website. However, search engines have since realised that webmasters were manipulating the results by stuffing their pages with irrelevant keywords and have since developed more complex ranking algorithms to combat spam.
So, what has changed?
To stay on top, a website’s SEO needs to constantly change and adapt to match the changing algorithms used by the search engines. In the early 2000s, Google introduced paid search ads in the form of AdWords. An advertiser pays to have their advert appear on Google’s search engine results page alongside the organic (unpaid) search results. A company can improve the results of an unpaid search result by using SEO tactics.
Search results are now highly specific and dynamic to each user. From 2004-2007, local content got a boost when search engines improved their results based on where the queries were coming from in the world. And, with a whopping 900% increase in “near me” searches between 2013-2017 you can’t afford to not optimise your website’s SEO for local.
SEO for mobile
Around 2015, search engines included speed and mobile-friendliness in their webpage ranking. This was as mobile searches overtook desktop searches for the first time. With this, Google once again adapted their search engine to allow people to search on their mobile phones and tablets and adopted mobile-first indexing in 2018. This means that Google rank and index websites primarily using the mobile version. As of 2019, this became the default for all new web domains.
A person’s search behaviour differs from mobile to desktop due to the experience. On a mobile, a person may be in town and quickly need to search for a place to replace their flat tyre; they need the information to load fast. A mobile phone’s screen is also a lot smaller and displays fewer results before the user needs to swipe. Therefore, they are more likely to choose the first few results rather than continue to scroll to the bottom of the page. In contrast, a desktop user is more likely to have more time to browse the search results – reading the information and different listings before making their selection.
With this in mind, you need to tailor your SEO strategy to cater to both desktop and mobile users. Your website needs to have a responsive and user-friendly design and should load quickly (keep your website’s elements small to allow for this). As ever, you need to ensure you are incorporating the right keywords, but you now also need to consider voice search keywords. A staggering 27 percent of the global online population are now using the voice search feature on their mobile phones. So this means you should be using conversational language, long-tail keyword phrases (long search queries of 5+ words which are more specific), and optimise for Rich answers (the blocks of information normally found above the search results on your Google SERP) by including short, concise answers of 30 words or less in your content.
Be social
With the advent of social media, a company’s SEO can be indirectly affected by its social media presence. By sharing links across your social media platforms and getting current customers to share your links too, you can increase your brand’s awareness and exposure. Search engines will pick up on this social activity and come to the conclusion that your posts are useful to your target market. Which in turn will lead to an improvement in the ranking of your website.
Take Home
Going forward, user experience will be critical. The longer a visitor stays on your site and the more frequently they visit will positively impact how search engines rank your site. By focusing on SEO, content creation, and social media, a business can increase traffic to its website. If you want to find out how SEO can help to improve your website’s traffic, contact us at GPS Online.